The realm of space exploration has given us a glimpse into the universe’s vast expanse, unraveling mysteries and unveiling breathtaking wonders that were once beyond our reach. Among the most remarkable tools in this cosmic journey are space telescopes, designed to capture the beauty and secrets of the universe from beyond the confines of Earth’s atmosphere. In this blog, we’ll delve into the contributions of three renowned space telescopes: Hubble, Kepler, and James Webb, and explore the groundbreaking discoveries they have facilitated.
The Hubble Space Telescope: Unveiling the Cosmic Canvas
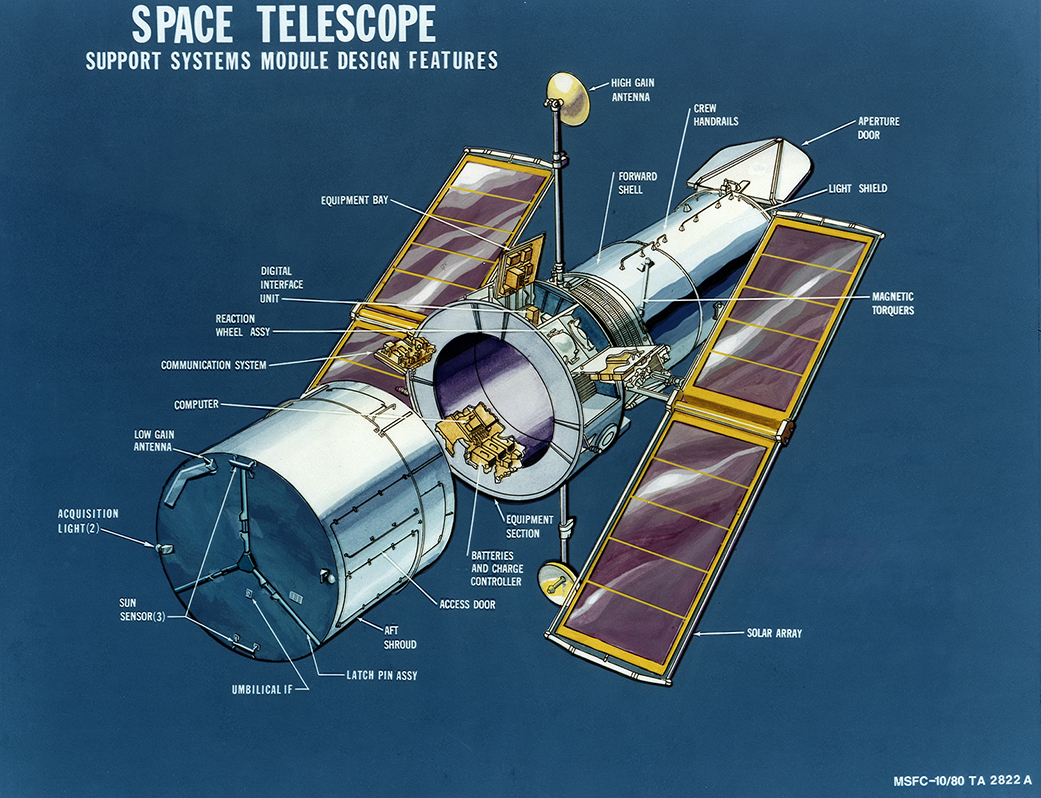
Launched into orbit on April 24, 1990, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) quickly became an icon of space exploration, capturing some of the most awe-inspiring images ever taken. Named after astronomer Edwin Hubble, this telescope’s primary mirror measures 2.4 meters in diameter and is positioned above Earth’s distorting atmosphere, allowing it to capture images with unprecedented clarity.
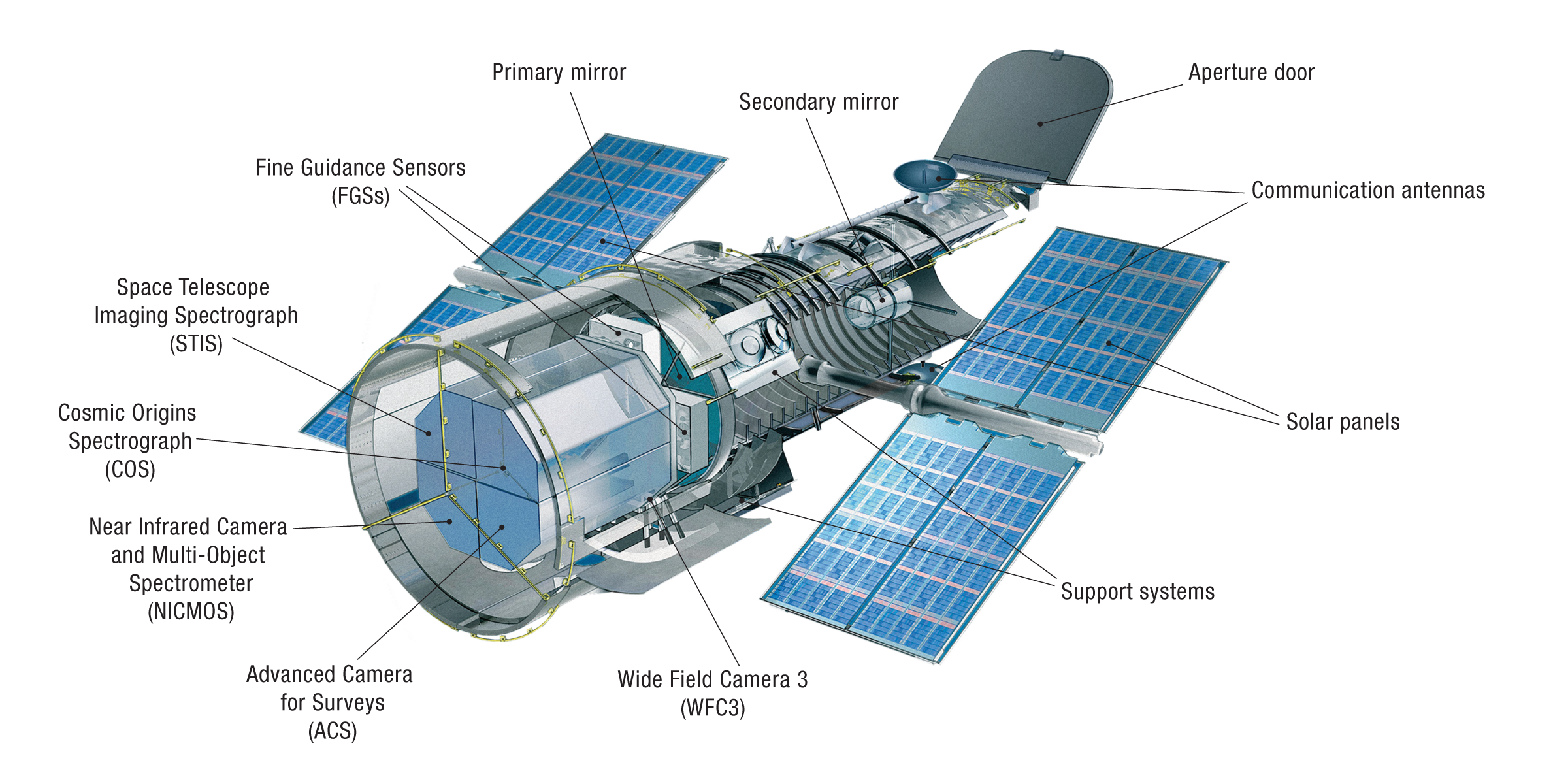

One of Hubble’s most significant contributions is its role in accurately measuring the rate of expansion of the universe, known as the Hubble Constant. By observing distant galaxies and their redshifts, Hubble provided vital data that led to a refined estimate of the universe’s age and offered insights into its future.
Hubble’s Deep Field images, captured over multiple exposures and showing a seemingly dark and empty patch of space, revealed a staggering multitude of galaxies, some of which existed just a few hundred million years after the Big Bang. This discovery not only highlighted the vastness of the universe but also deepened our understanding of its evolution over billions of years.
In 1994, Hubble unveiled Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9’s collision with Jupiter, providing an unprecedented view of this cosmic cataclysm. Additionally, its observations of exoplanet atmospheres and distant galaxies helped scientists refine models of star formation, galaxy evolution, and the composition of the cosmos.
The Kepler Space Telescope: Hunting for Exoplanets
Launched on March 7, 2009, the Kepler Space Telescope revolutionized our understanding of the universe by focusing on a specific task: hunting for exoplanets – planets outside our solar system. With its precise photometric measurements, Kepler identified exoplanets by detecting the minute dimming of starlight as a planet passed in front of its host star.

Kepler‘s findings fundamentally altered our understanding of the prevalence of exoplanets, demonstrating that they are common in our galaxy. One of its most astonishing discoveries was Kepler-452b, a planet with similarities to Earth and located within its star’s habitable zone, where conditions might allow for liquid water to exist on the surface – a potential host for extraterrestrial life.
By the time Kepler’s primary mission ended in 2013, it had identified over 2,600 confirmed exoplanets and nearly 3,000 more candidates awaiting confirmation. Its legacy lives on through its data, shaping our understanding of planetary systems and guiding the design of future space telescopes.

The James Webb Space Telescope: A New Frontier of Discovery
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope specifically designed to conduct infrared astronomy. Its high-resolution and high-sensitivity instruments allow it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble Space Telescope. the JWST is a collaborative effort between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). This revolutionary telescope is designed to succeed the Hubble Space Telescope and promises to expand our understanding of the cosmos even further.
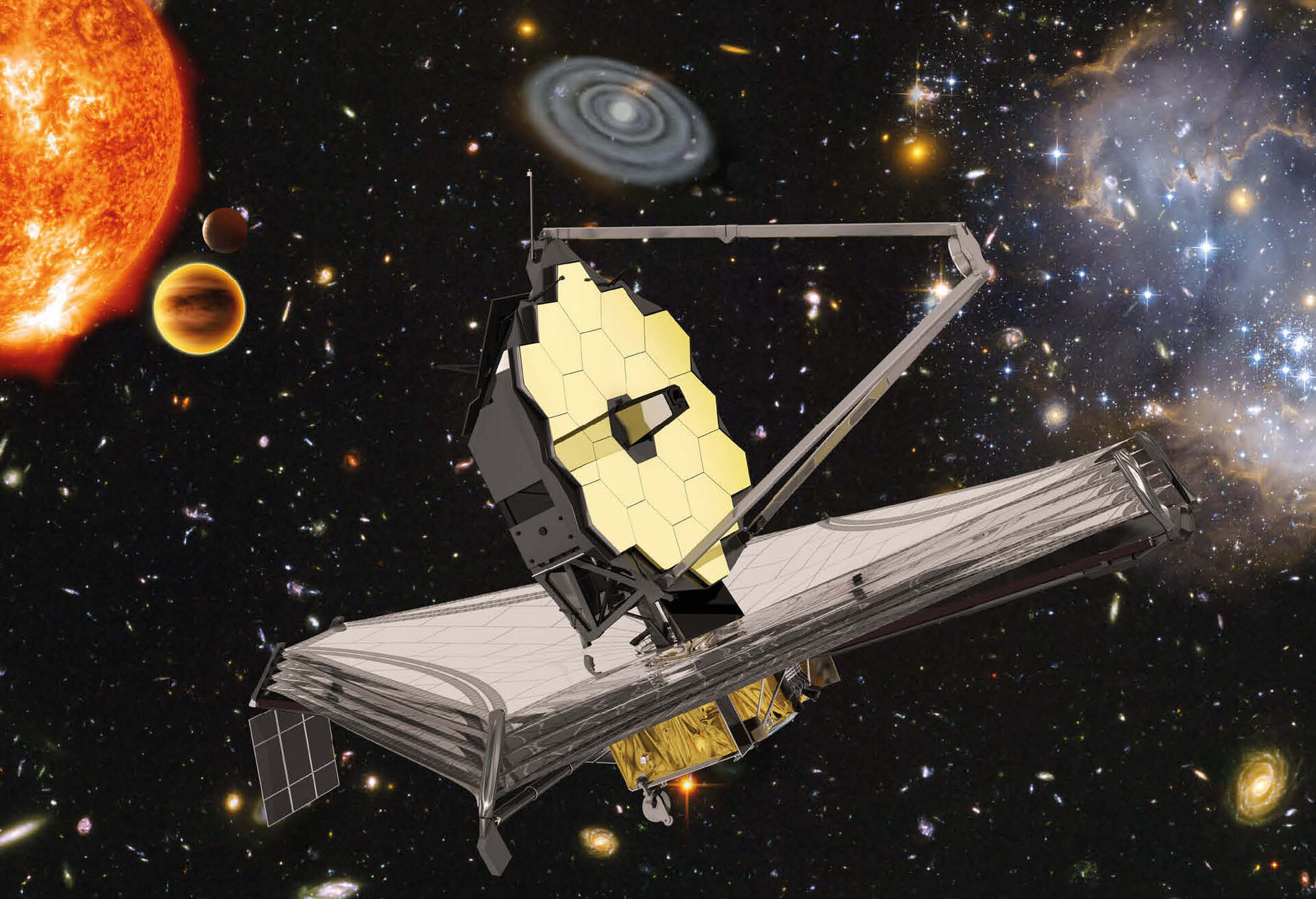

The JWST is equipped with a larger primary mirror, spanning 6.5 meters, and infrared instruments that allow it to peer through dust clouds, revealing previously hidden cosmic phenomena. Its enhanced capabilities are expected to provide insights into the formation of galaxies, stars, and planetary systems, as well as the characteristics of exoplanet atmospheres.
One of the JWST’s primary goals is to observe the universe’s early stages, including the formation of the first galaxies and stars. By studying the light from these distant objects, scientists hope to unravel the mysteries of the universe’s origins and evolution.
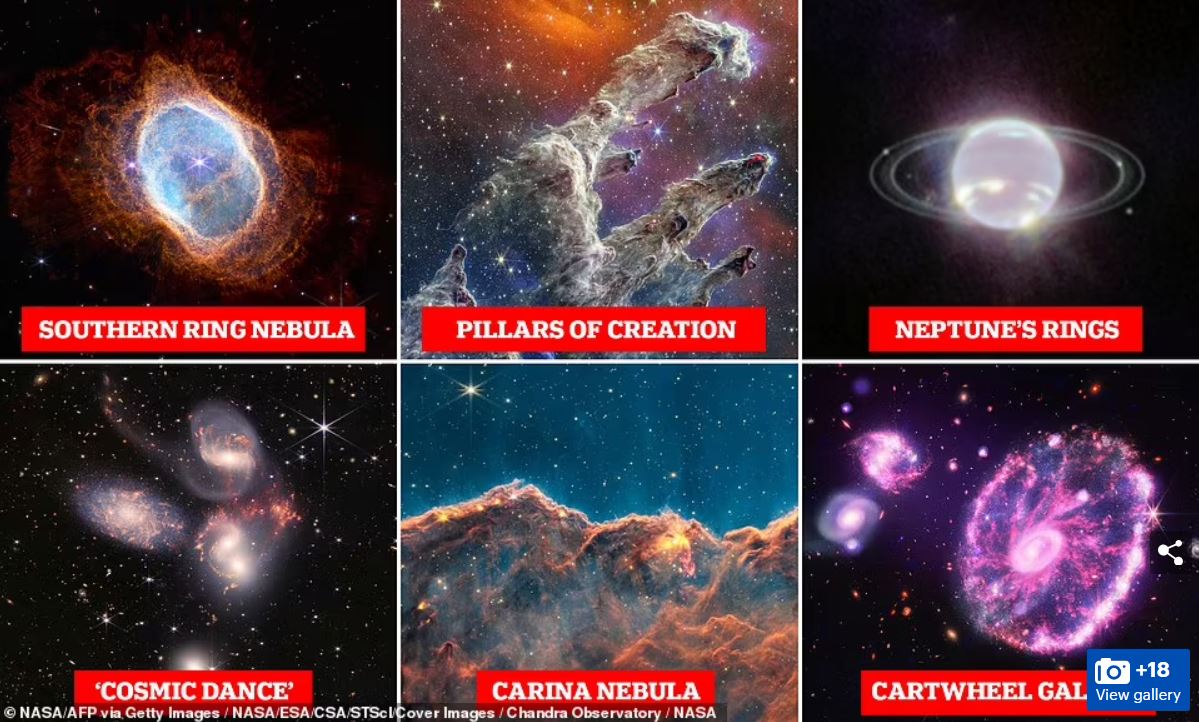

Conclusion
Space telescopes like Hubble, Kepler, and the James Webb have revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos, expanding the horizons of human knowledge and inspiring generations to look beyond our terrestrial realm. Hubble’s awe-inspiring images, Kepler’s exoplanet discoveries, and the breathtaking discoveries and paradigm-shifting insights by the James Webb Space Telescope all serve as testaments to the human spirit of exploration and curiosity.
These space telescopes remind us that the universe is a vast, interconnected tapestry, and every image and piece of data contributes to the mosaic of our understanding, driving us forward in our quest to comprehend the universe’s grandeur and intricacies.

